Staying competitive is not an easy task for companies. Good organisation, accounting, and good intentions are not enough. In order to meet the demands of the market, business analysis is essential for maintaining long-term business development and direction. Business analysis will take into account several important aspects that will show the extent to which the business will develop and whether it is running effectively.
This article provides guidance on the question what is business analysis?
The business analysis discipline has evolved over the last twenty years and is still an important practice of enabling change in an organisational context, by defining needs and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders. Whilst, technology will be important for many solutions, there is a need to consider a wider aspect of change in the area of process, organisation, information and people (POPIT) to meet business outcomes.
to meet business outcomes.
Organisations want assistance in finding potential solutions to business issues and opportunities, sometimes where information technology may not prove to be the answer. It has become apparent that this requires the role of the business analyst to support business managers in providing the necessary assistance.
With the rise of digital transformation in organisations, there is an increasing focus and awareness of using investment funds wisely and delivering the business benefits predicted for business change initiatives.
Before we get into more detail, let’s understand what is IIBA and BABOK in relation to business analysis.
Table of Contents

What is IIBA?
The International Institute of Business Analysis, also known as IIBA , is a non-profit association that facilitates the business analyst, who are the professionals that deals with business analysis.
, is a non-profit association that facilitates the business analyst, who are the professionals that deals with business analysis.
The business analysis profession has matured through the establishment of business analysis industry bodies and business analysis certifications.
Prior to these business analysis industry bodies and business analysis certifications ; some business analysts may have had difficulties in their organisations explaining the roles and the value they provide.
; some business analysts may have had difficulties in their organisations explaining the roles and the value they provide.
What is BABOK?
The Business Analysis Body of Knowledge Guide, also known as the BABOK Guide , is the body of business analysis knowledge published by IIBA (International Business Analysis Institute). The BABOK Guide is composed of six areas of knowledge, a chapter containing the fundamental skills for the business analyst and a chapter with 34 techniques for the practice of business analysis
, is the body of business analysis knowledge published by IIBA (International Business Analysis Institute). The BABOK Guide is composed of six areas of knowledge, a chapter containing the fundamental skills for the business analyst and a chapter with 34 techniques for the practice of business analysis .
.
The BABOK Guide also provides a basis for understanding the six fundamental business analysis concepts: change, need, solution, stakeholder, value, and context via the Business Analysis Core Concept Model (BACCM).
What is Business Analysis?
Business analysis includes a set of techniques that are used as a link between some business participants in order to understand the structure, rules, and functions of the organisation. In the end, business analysis is expected to offer optimal solutions that will allow the organisation to achieve its goals. For successful business analysis, various methods are used. It is worth noting that sometimes the analyst uses several different methods to perform one task.
In short, business analysis is an investigation into the state of affairs of a company. By conducting business analysis, you can identify business needs and determine solutions to deal with various business problems. This is very useful because both the behaviour of the customers and the market itself is always subject to change. A company does not remain the same all the time. Some of the questions that are addressed during business analysis are:
- Where are opportunities, and how do we use them?
- Where do we see threats, and how do we tackle them?
- Opportunities for growth?
- Are there points for improvement?
The business analysis consists of two parts: the internal and external analysis.
- Internal business analysis – this is focused on the company, and it involves investigating the status of the image, process, organisation, information, people, information technology, customers, approach, and the position of the brand, among other things;
- External business analysis – focuses on the opportunities in the market, the position in relation to competitors, and the demand for the desired results.
Business Analysis Knowledge Areas
The business analysis is divided into six major areas of knowledge, as defined in BABOK. They are:
Business Analysis Planning and Monitoring
Business analysis planning and monitoring includes all the work of organising as the techniques, tools, and business analysis activities will be used in practice. In this planning, care is taken to identify whether the technique or practice is suitable for the initiative. Especially because not every project should use the same tools and techniques. Planning is also expected to identify the means by which the team will monitor the results of the business analysis itself.
includes all the work of organising as the techniques, tools, and business analysis activities will be used in practice. In this planning, care is taken to identify whether the technique or practice is suitable for the initiative. Especially because not every project should use the same tools and techniques. Planning is also expected to identify the means by which the team will monitor the results of the business analysis itself.
The Elicitation and Collaboration
Elicitation and collaboration includes all the work to identify, document, and validate the wishes and desires that stakeholders expressed during the survey activities. Elicitation work can be formal or informal. Elicitation is of fundamental importance to validate whether the evident wishes can be understood as real needs.
includes all the work to identify, document, and validate the wishes and desires that stakeholders expressed during the survey activities. Elicitation work can be formal or informal. Elicitation is of fundamental importance to validate whether the evident wishes can be understood as real needs.
Requirement Life Cycle Management
Requirements life cycle management involves all the work of managing the artefacts produced and/or used during the work of business analysis. This is where results and deliverables are communicated. All communication takes into account who communicates, what should be communicated, and when. All are well done to avoid any problem.
involves all the work of managing the artefacts produced and/or used during the work of business analysis. This is where results and deliverables are communicated. All communication takes into account who communicates, what should be communicated, and when. All are well done to avoid any problem.
Strategy Analysis
The strategy analysis comes to identify the business need correctly. That is, the problem or opportunity that business analysis is trying to solve or accomplish. It is also necessary to identify the nature of the solution that meets the business need and justifies the investment required to deliver the solution.
comes to identify the business need correctly. That is, the problem or opportunity that business analysis is trying to solve or accomplish. It is also necessary to identify the nature of the solution that meets the business need and justifies the investment required to deliver the solution.
The Requirements Analysis and Design Definition
Requirements analysis and design definition involves working to analyse in more depth what the interested party manifests as needs. This is where requirements are modelled according to the need and/or degree of abstraction required. It is in this area of knowledge that most modelling techniques are used. For example, use cases, data flow diagrams, diagram of entities and classes, and so on.
involves working to analyse in more depth what the interested party manifests as needs. This is where requirements are modelled according to the need and/or degree of abstraction required. It is in this area of knowledge that most modelling techniques are used. For example, use cases, data flow diagrams, diagram of entities and classes, and so on.
The Solution Evaluation
Solution evaluation is about ensuring that the solution meets the needs of the business and its stakeholders. It also ensures that the organisation is ready to use and realise all the potential value that the solution offers. In the evaluation and validation of the solution, interested parties must participate in activities that validate the effectiveness of the solution even before it goes into production
is about ensuring that the solution meets the needs of the business and its stakeholders. It also ensures that the organisation is ready to use and realise all the potential value that the solution offers. In the evaluation and validation of the solution, interested parties must participate in activities that validate the effectiveness of the solution even before it goes into production

What is a Business Analyst?
The person who conducts business analysis is a business analyst.
A business analyst is a person who acts as a link between various departments and members working in an organisation. The business analyst analyses, communicates, and validate the need for change in policies, processes, or information system. The business analyst is the person that understands the problems of an organisation and searches for solutions.
is a person who acts as a link between various departments and members working in an organisation. The business analyst analyses, communicates, and validate the need for change in policies, processes, or information system. The business analyst is the person that understands the problems of an organisation and searches for solutions.
Job titles for business analysis practitioners include not only business analyst, but also business systems analyst, systems analyst, requirements engineer, process analyst, product manager, product owner, enterprise analyst, business architect, management consultant, business intelligence analyst, data scientist, and more. Many other jobs, such as management, project management, product management, software development, quality assurance and interaction design rely heavily on business analysis skills for success.
A business analysts may find themselves working in the following situations:
- Modern organisations are increasingly focusing on strategic issues. A business analyst, understanding this need, is an expert in analysing the organisation’s strategic goals. Advises senior management on all issues of the necessary policies and effective political decisions. It happens that a particular organisation needs to introduce changes in order to solve the business problems that the strategist has found. In this situation, the business analyst begins to analyse goals, processes, and resources. He further suggests ways to upgrade or improve.
- An ancient problem in business is how to get the maximum return on expensive investments in the IT field. In this case, analysts must understand and determine all the requirements for IT systems. This type of analyst is invited already when the final decision about the changes has already been made.
Business analysis is directly related to a thorough analysis of requirements. This is aimed at specific changes in the organisation to achieve the designated strategic results. These changes include changes in the strategy that was approved earlier, in politics, in information systems, and structure.
Role and Responsibilities of a Business Analyst
The core responsibilities of a business analyst include:
- Investigating business systems, taking a holistic view of the situation; this may include examining elements of the organisation structures and staff development issues as well as current processes and information technology;
- Evaluating actions to improve the operation of a business system. This may require an examination of organisational structure and staff development needs, to ensure that they are in line with any proposed process redesign and information system development;
- Document the business requirements for the IT system;
- Elaborate requirements, to support the needs of the business users during the development of the solution;
- Some business analysis roles may extend into other areas, possibly the strategic analysis or systems analysis activities described above. This may be where business analysts are in a more senior role or choose to specialise. These areas are:
- Strategy implementation – the business analysts works closely with senior management to help define the most effective business system to implement parts of the business strategy;
- Business case production – more senior business analysts usually do this, typically with assistance from a financial specialist;
- Benefits realisation – the business analysts carry out post-implementation reviews, examine the benefits defined in the business case and evaluate whether or not the benefits have been achieved;
- Specification of information technology requirements – typically using standard modelling techniques such as use case modelling, data modelling or user story writing.

Why a Business Analysis is Important to a Company
Good business analysis leads to targeted and effective improvement actions. This has or can have an effect in many areas. For example, the competitive position, lower costs, higher customer satisfaction, a shorter lead time, improvement of workplaces, and improvement of cooperation. Issues such as leadership, management systems, the entire business process, staff, and the product can be improved and strengthened.
A quarter to half of the costs of an organisation is in activities that are hardly visible. Examples of this include loss of working time because materials have to be sought, too much and/or too long meetings, inadequacy in solving problems and complaints, or poor cooperation.
By making this type of thing visible, savings can be made quickly and effectively. Therefore, a more positive result will be achieved in the shortest time both internally and externally. The main purpose of business analysis is to reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and improve productivity. Other effects of the business analysis can be:
- Reducing labor costs by simplifying processes;
- Shorten waiting times without loss of quality;
- Improve information provision;
- Reduce inventory without reducing delivery reliability;
- Develop leadership.
Benefits of Business Analysis
In accordance with the understanding of business analysis itself, there are several objectives and benefits of business analysis. To find out the benefits for all parties, see the information below.
Benefit for Entrepreneurs
Entrepreneurs must practice business analysis if they want to minimise the initial risks of their enterprise. They do this through a critical analysis of their business models, products, services, and results. Models like Business Model Canvas, Lean Startup, and Design Thinking have become popular in recent years because they empower lay professionals to make more assertive decisions. Nowadays, the market has evolved a lot, making entrepreneurs invest in hypothesis tests instead of writing Business Plans.
Benefit for Managers
Managers should practice business analysis if they want to understand the cause-and-effect relationships between business capabilities and results. In this case, it is common to see analysis tools such as SWOT, Business Case, Project Charter, Schedule, among many others, being used daily by management teams. However, it is very likely that these managers delegate the analysis activity to their technical experts and delay their decisions due to limited knowledge of analysis tools.
Benefits for Business Consultants
Consultants should practice business analysis when they need to understand the current scenario, its limitations, and related causes. They should also facilitate the construction of a future scenario and its related benefits, as well as identify resources/solutions and transformation strategies for the effective improvement of the business.
Benefits for Human Resources Consultants
The human resource must practice business analysis, as they are a specific case of business consulting, whose solutions involve knowledge of people management and labor operations. An HR consultant, who practices Business Analysis, would never “take an order” to hire new professionals for a given area. He first has to question the real business problems and validate the hiring as an effective solution to the problem.
Project Managers
A project manager must practice business analysis if he wants to understand how a product strategy will support a business strategy through a correct process strategy. It is the effective orchestration of these three strategic perspectives that will maximise the chances of success for a complex project. Not the simple sequencing of activities and allocation of resources.
Benefits for Software Developers
Software developers must practice business analysis when analysing objectives, constraints, capabilities, rules, and examples of what will be designed and implemented. The number of failures and production time will be reduced with the proper training of the team in business analysis techniques and tools. In the case of developers, the greatest benefit is to make them competent to question what is demanded with rational arguments and to avoid wasting the production of what is not necessary for a product.

Why the Role of a Business Analyst is Important in Business Analysis
Every company is looking for more efficiency in the use of its resources. Also, every company is looking for ways of the optimisation of its workforces and increased productivity. One of the modern ways of achieving all this is by improving the technological tools available. Here is where a business analyst comes in.
This professional makes work more efficient, effective, and productive. This is because better systems reduce costs, increase productivity, and facilitate work. This also increases employee motivation, which is essential in a competitive and rotating market today. The role of the business analyst is strategic. That is, solving the organisational communication problems that exist between the management and technology areas.
In addition, it is necessary to remember that the business analyst works in all hierarchical spheres of a company. This is because his function demands that he is always aware of everything so as to identify problems before they even arise.
Tips for Good Business Analysis
Good business analysis is a major investment in any company that wants to improve its operation. However, as a business analyst, you will need to make a good analysis so as to give the right solution. Here are some tips to make a good business analysis.
Do it on Time
It often happens that a company analysis is only chosen when the signals are red. These are often financial signals. The big disadvantage is that the focus is then largely on the finances, and there is much less room for the entrepreneur and the product. The damage has already been done, and previous signals have been missed or hidden. Practical signals such as payment reminders, overdue maintenance, or simply worried faces. If you have a business analysis made at times when things are going well, you can make a profit.
Choose the Right Model
There are different kinds of models and techniques an analyst can use to do a business analysis. Choose one that suits the company you are inserted in. An example is the SWOT analysis. You investigate the entire industry in which you work. You see the opportunities and threats. Therefore, SWOT analysis is called the ‘strength weakness analysis.’
Clear Knowledge of the Company
You cannot give a solution if you don’t have enough knowledge about a company. As a business analyst, you are required to do thorough research about the company before coming up with any resolution. Even a single point left out can have a huge impact on the business. Always take your time and ensure that every important detail is captured.
Business Analysis is not just about Numbers
As mentioned in the first point, a business analysis that is made when things are not going well, then it will be about numbers. However, a company is much more than just numbers. It is about people. Both internally and externally. As an analyst, it’s good to involve everybody in the business analysis. A personal analysis of leaders and employees is often just as important.
Determine what is Valid in Contact with the Business Areas
Not all opinions will always be valid and will lead to the success of the project/product. This is one of the main points for success in the job. Knowing how to determine what desires are needed is very important in achieving a company’s goal.
Examples of Business Analysis
The strategic planning method that is often used to evaluate the feasibility of a business venture is the SWOT method. SWOT analysis is a method for evaluating weaknesses, strengths, opportunities, threats, and speculations in accordance with their lengths, Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, and Threats.
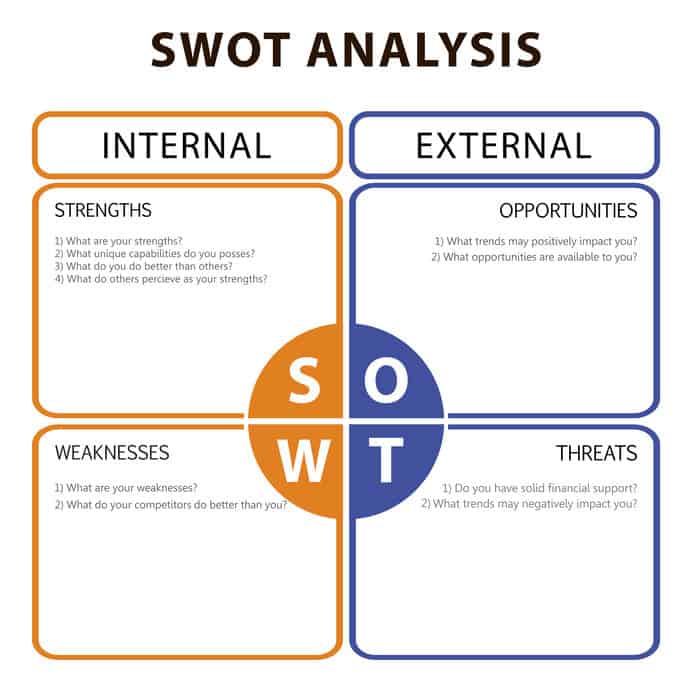
Strength
Strength in an organisation is a project or concept. The strengths analysed here are factors that exist in the organisation, project, or business concept. The following are just but some of the guidelines that can be used to fill this analysis:
- What are the advantages of a company?
- What makes the company better than others?
- What are the things that consumers see as an advantage?
Weakness
Weakness is a weakness found in an organisation. What is seen here is the weakness in the project, organisation, and concept. The following are some of the guidelines that can be used to fill this analysis:
- What factors cause loss of sales?
- What can is it that can be improved in the company?
- What should be avoided in the company?
- What are the things that consumers see or feel like a weakness in the company?
- What are the competitors doing to be better?
Opportunities
Opportunity is an opportunity owned by an organisation to develop in the future. In the SWOT analysis, that is highlighted, starting from government policies, competitors, to market conditions. The following are some of the guidelines that can be used to fill this analysis:
- What are the opportunities that the company has?
- What development trends are in line with the company?
Threats
Threats are challenges or threats that come from outside the organisation. The point here is a variety of threats that come and possibly occur so as to interfere with business effectiveness. The following are some of the guidelines that can be used to fill this analysis:
- What are the obstacles facing the company?
- What competitive advantage does the competitor have?
- Are government regulations that are going to hinder the development of the company?
Conclusion – What is Business Analysis ?
So what is business analysis ? this article has provided an explanation of the meaning of business analysis, it’s types, benefits, and example of business analysis. It is evident that business analysis plays a key role in company growth and productivity. Doing business analysis is the first thing that must be done to deal with the various possibilities that will occur during the running of the business.


